China is Indonesia’s largest source of imports and its largest export market. Indonesia is also an important investment destination for Chinese companies.
For Chinese companies operating in Indonesia, tax compliance is of paramount importance. This article will provide a brief overview of Indonesia’s tax system to assist investors in making informed decisions and help companies quickly grasp the tax framework.
Indonesian Tax System Framework:
Management Authority: The Directorate General of Taxation (DGT) under the Ministry of Finance is responsible for tax administration.
Collection and Management System: A self-assessment system is implemented, placing significant responsibility on taxpayers.
Legal Framework: Based on the Income Tax Law, Value Added Tax (VAT) and Luxury Goods Tax Law, General Tax Law and Procedures, and relevant government regulations.
Main Tax Categories:
01 Corporate Income Tax
Indonesia levies a global income tax on tax-resident enterprises (companies registered in Indonesia and foreign companies with a permanent establishment in Indonesia).
Standard Tax Rate: 22%
Incentives:
-
Micro and small enterprises with annual revenue not exceeding 50 billion rupiah can enjoy a 50% tax base reduction.
-
Specific micro-enterprises are subject to a simplified tax rate of 0.5%.
Annual Tax Filing: Once a year, with quarterly prepayments required.
02 Individual Income Tax
Tax Obligations for Residents: Indonesian residents (individuals who reside in Indonesia for a certain period or have a domicile in Indonesia) are required to pay taxes on global income; non-residents are only taxed on income sourced from Indonesia.
Resident Tax Rate Structure:
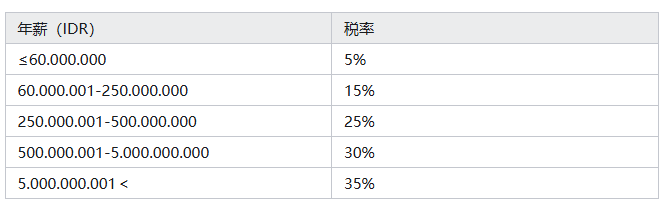
Non-Resident Flat Tax Rate: 20% (levied on total income without the possibility of deducting expenses)
Note: Income such as bonuses, allowances, dividends, and interest should be included in the total personal income.
03 Withholding Taxes
These are income taxes withheld in advance. When making specific payments, the payer is obligated to withhold the tax and file on behalf of the payee.
Scope of Application: Salaries, wages, service fees, rent, dividends, interest, royalties, etc.
Withholding Tax Rates:
-
Domestic payments: Withholding tax rates range from 2% to 15%.
-
Payments to non-residents: Typically 20%, but lower rates may apply under bilateral tax treaties.
Note: Failure to fulfill withholding obligations may result in fines and late payment penalties. For payments to suppliers exceeding a certain amount, companies are required to withhold a 2% service tax (PPh 23).
04 International Tax Agreements Tax
Indonesia has signed Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTA) with over 70 countries.
Incentives: These agreements may exempt or reduce withholding tax rates on dividends, interest, and royalties.
Eligibility Requirements: A Certificate of Domicile (CoD) from the taxpayer’s country of residence is required.
Note: The complete CoD documentation must be submitted before payment. Failure to submit on time may result in the inability to enjoy tax benefits.
05 Value Added Tax (VAT)
Standard Tax Rate: 11% (The rate may increase to 12% from 2025 onwards).
Taxable Entities: Businesses with annual turnover exceeding 500 million rupiah are required to register as VAT taxpayers.
Exemptions: Basic necessities, healthcare, education, finance, and other sectors are exempt.
Note: For certain specific industries or types of transactions, Indonesia implements a “final VAT” system, where VAT is calculated at a specific rate. A legal “tax invoice” must be issued; otherwise, significant fines may apply.
06 Luxury-Goods Sales Tax (LST)
This tax is levied on specific high-end products.
Applicable Goods: Include luxury cars, yachts, private jets, and high-end residences.
Tax Rates: The rates range from 10% to 95%, depending on the type and specifications of the goods.
Note: The LST is an additional tax on top of VAT.
07 Customs & Excise
Customs Duties: Applicable to imported goods, with rates typically ranging from 0% to 40%, based on the Harmonized System (HS) code of the goods.
Excise Taxes: Mainly levied on tobacco products, alcoholic beverages, sugary drinks, etc.
Note: Customs compliance and Certificates of Origin (COO) are crucial, as they affect tariff preferential treatments.
08 Stamp Duty (Bea Materai)
Stamp duty is a tax levied by the Indonesian government on civil documents and court-used documents, aimed at legalizing transactions and serving as evidence.
Scope:
-
Various types of agreements, certificates, statements, and their copies;
-
Notary documents and their originals (Grosse), copies, and excerpts;
-
Land deeds and their copies, excerpts issued by Land Deed Officials (PPAT);
-
Securities in various forms and names;
-
Securities transaction documents, including futures contracts;
-
Auction documents, such as bid sheets, minutes, copies, and their originals (Grosse).
Purpose: The collection of stamp duty ensures the legality and validity of documents, serving as an official record of transactions and contracts.
09 Land and Building Tax (PBB)
This is an annual property tax levied on the ownership or usage rights of land and buildings.
Tax Base: The taxable value of land and buildings (NJOP) as determined by the government.
Tax Rate: Generally 0.5%.
Payers: Property owners or actual users.
Note: Specific economic zones or industrial zone projects may apply for PBB exemptions or reductions.
Tax Concessions
The Indonesian government offers various tax incentives to encourage investment and innovation.
Investment Holiday: Eligible investments in specific industries can enjoy a full exemption from corporate income tax for up to 20 years.
Investment Allowance: Qualified investment projects can benefit from tax base deductions.
Additional Deduction for R&D Expenses: Specified R&D costs can be deducted at an additional rate of 300%.
These policies are key to reducing the effective tax burden and enhancing the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of projects.
Approval Process: Approval from the Investment Coordinating Board (BKPM) is required. The application and maintenance of tax concession eligibility involve strict procedures and documentation requirements, which need to be precisely managed to ensure compliance and enjoyment of the benefits.
Note: Indonesia may announce new tax policies for 2025 soon. All information should be based on official announcements.
Indonesia’s stable and flexible tax system provides an attractive business environment for foreign investors. Combined with its abundant natural resources, large market size, and continuously improving infrastructure, Indonesia offers a gateway to the Southeast Asian and global markets, presenting unprecedented investment opportunities.
-End-
Seize the Opportunity and Invest in Indonesia—A Call to Action for Manufacturing Decision-Makers
In the current reshaping of the global trade landscape, inaction is the most expensive strategy! As the largest economy in ASEAN, Indonesia is offering a “zero-time-difference” production launch solution for manufacturing through its national economic zones and ready-to-use standardized factories:
-
Tariff Breakthrough
Bypass the 125% additional tariffs imposed by the U.S. on China. Relying on the Indonesia-ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), enjoy zero-tariff export benefits for 90% of goods within the region.
-
Cost Lock-in
-
Tax Policy: Special Zone enterprises enjoy a 15-year corporate income tax reduction (full exemption for the first 5 years, halved for the next 10 years) and full exemption on import duties for equipment.
-
Labor Costs: 38% of the workforce is under 25 years old, with an average monthly wage in manufacturing only one-third of that in China.
-
Energy Costs: Electricity prices are approximately 0.50 RMB per unit, with peak rates at 0.75 RMB.
-
Employee Social Security: Health insurance is paid at 1% of wages by both the employer and employee, pension insurance is paid at 8.4% of wages by the employer, and work injury insurance is paid at 0.24% of wages by the employer (totaling less than 10%).
-
Ready-to-Use Facilities
1 million square meters of high-standard factories are available for “immediate rent and use” in the Batang Economic Zone in Central Java:
-
Complete Infrastructure
-
Adjacent to Highways
-
Free Trade Zone
-
Green and Energy-Efficient Factories
-
“One-Stop” Services
At this moment, what is rarer than a “cost-effective location” is a “strategic springboard” resource.
Please contact our investment team immediately to obtain a customized implementation plan—starting the race while others hesitate is the true competitive advantage!
Seize the opportunity and invest in Indonesia—A call to action for manufacturing decision-makers.





